暂无AI摘要
暂无AI摘要
问题
请编写一段Python代码,使其能调用C程序。
思路
这是一道课后作业,在题目里并没有说明怎么算用Python调用C程序,所以我考虑了以下两点:
- 使用Python调用C代码生成的可执行文件(windows下是exe文件)
- 使用Python调用C代码生成的共享库(windows下是dll文件)
实验环境
windows11、Python3.9、pycharm
主要用到的包
ctypes、subprocess、os
代码实现
此代码包含的内容:
- 使用python代码调用c可执行文件(exe)
- 使用python代码调用c共享库(dll)
- 使用python代码创建并编译c代码的过程
import os
import ctypes
import subprocess
def create_c_file(file_name):
"""
Create a C file containing code to calculate the GCD of two integers.
Args:
file_name (str): The name of the C file to be created.
"""
with open(file_name, 'w') as f:
f.write('''
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/**
* @brief 计算两个整数的最大公约数
*
* @param a 第一个整数
* @param b 第二个整数
* @return int 两个整数的最大公约数
*/
int gcd(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
/**
* @brief 程序的主函数
*
* @param argc 命令行参数的数量
* @param argv 命令行参数的数组
* @return int 返回0表示程序正常结束
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s num1 num2\\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
int num1 = atoi(argv[1]);
int num2 = atoi(argv[2]);
int result = gcd(num1, num2);
printf("GCD of %d and %d is %d\\n", num1, num2, result);
return 0;
}
''')
def compile_c_file(file_name, output_name, shared=False):
"""
Compile the C file into an executable or shared library.
Args:
file_name (str): The name of the C file to be compiled.
output_name (str): The name of the output file (executable or shared library).
shared (bool): Whether to compile as a shared library. Default is False.
"""
args = ['gcc']
if shared:
args.extend(['-shared', '-fPIC'])
args.extend(['-o', output_name, file_name])
subprocess.check_call(args)
def load_gcd_library():
"""
Load the compiled GCD shared library.
Returns:
ctypes.CDLL: The loaded GCD shared library.
"""
gcd_library = ctypes.CDLL('./gcd.dll')
gcd_library.gcd.argtypes = (ctypes.c_int, ctypes.c_int)
gcd_library.gcd.restype = ctypes.c_int
return gcd_library
def find_gcd(gcd_library, a, b):
"""
Calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of two integers using the GCD C library.
Args:
gcd_library (ctypes.CDLL): The loaded GCD shared library.
a (int): The first integer.
b (int): The second integer.
Returns:
int: The GCD of the two integers.
"""
result = gcd_library.gcd(a, b)
return result
def call_gcd_exe(file_name, num1, num2):
"""
Call the GCD executable with two integers as command-line arguments.
Args:
file_name (str): The name of the executable file.
num1 (int): The first integer.
num2 (int): The second integer.
Returns:
int: The return code of the subprocess call. 0 indicates success.
"""
return subprocess.call([file_name, str(num1), str(num2)])
def main():
"""
The main function of the Python script.
"""
c_file_name = 'gcd.c'
shared_library_name = 'gcd.dll'
executable_name = 'gcd.exe'
# Create and compile the C file into a shared library and an executable
create_c_file(c_file_name)
compile_c_file(c_file_name, shared_library_name, shared=True)
compile_c_file(c_file_name, executable_name)
# Test the shared library
gcd_library = load_gcd_library()
num1 = 56
num2 = 98
result = find_gcd(gcd_library, num1, num2)
print(f"Using shared library: GCD of {num1} and {num2} is {result}")
# Test the executable
ret_code = call_gcd_exe(executable_name, num1, num2)
if ret_code != 0:
print(f"An error occurred while calling the GCD executable. Return code: {ret_code}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
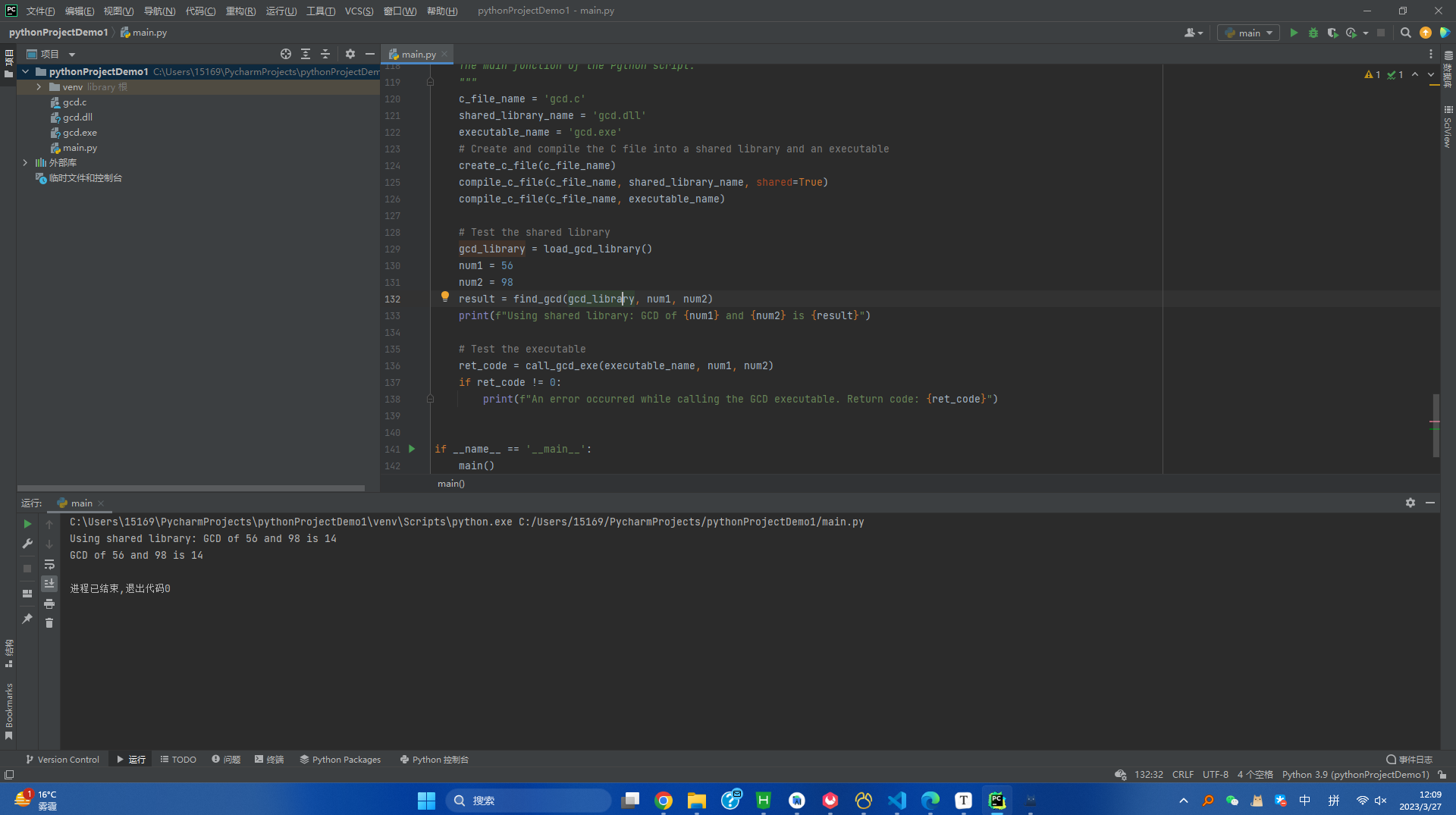
main()运行结果
原创文章,作者:白函,如若转载,请注明出处:https://wtboxes.com/article/36